This environment simplifies programming by orders of magnitude compared to the traditional blocky-based system. Additionally, the way Pybricks uses the DriveBase object makes your robot more reliable.
Sample competition code
You can find a sample competition code in my github repository: 2025 EduCup Masters - Attila Faragó.
Tasks
Challenge: Simulate a space rescue mission for a stranded astronaut crew.
- Build a Spaceship: Assemble Lego components to create a functional spaceship.
- Collect Cargo: Gather essential supplies (water, air, food) for the astronauts.
- Rescue the Crew: Guide the astronaut Lego figures to a safe location.
- Park the Robot: Guide the robot to a designated parking area.
Scoring: Points are awarded for completing each task, with bonuses for efficiency and correct spaceship assembly.
Robot actions
The robot navigates, collects and releases objects, and aligns itself with walls using sensors and motor control.
Here’s a breakdown of the robot’s actions:
- Initialization: The robot configures its motors, sensors, and settings. It defines functions for basic movements like turning, moving forward, and raising/lowering an arm.
- Part 1: The robot starts at a specific orientation facing south. It moves and turns to reach the North Wall, collects an object (R2), and then places it on another object (R1) while aligning itself with the East Wall.
- Part 2: The robot collects another object (R1) and places it on a designated spot.
- Part 3: The robot collects a third object (R3) and prepares to place it with other objects.
- Part 4: The robot gathers additional objects (R3, Fig3, Fig4, and a soda can) and places them strategically.
- Part 5: The robot collects a soda can and places it near a rocket.
- Part 6: The robot retrieves objects (Fig1, Fig2) and releases them.
- Part 7: The robot takes a soda can to a designated university
The robot uses a combination of movement, object manipulation, and wall-following strategies to execute these tasks efficiently.
Pybricks framework
- Pybricks
- Pybricks is Python and Block coding for smart LEGO® hubs. Run programs directly on the hub, and get full control of your motors and sensors.
For further details, documentation, programming environment and sample projects head to their website.
We are grateful to the developers of PyBricks and recommend that you try this framework out in the next season.
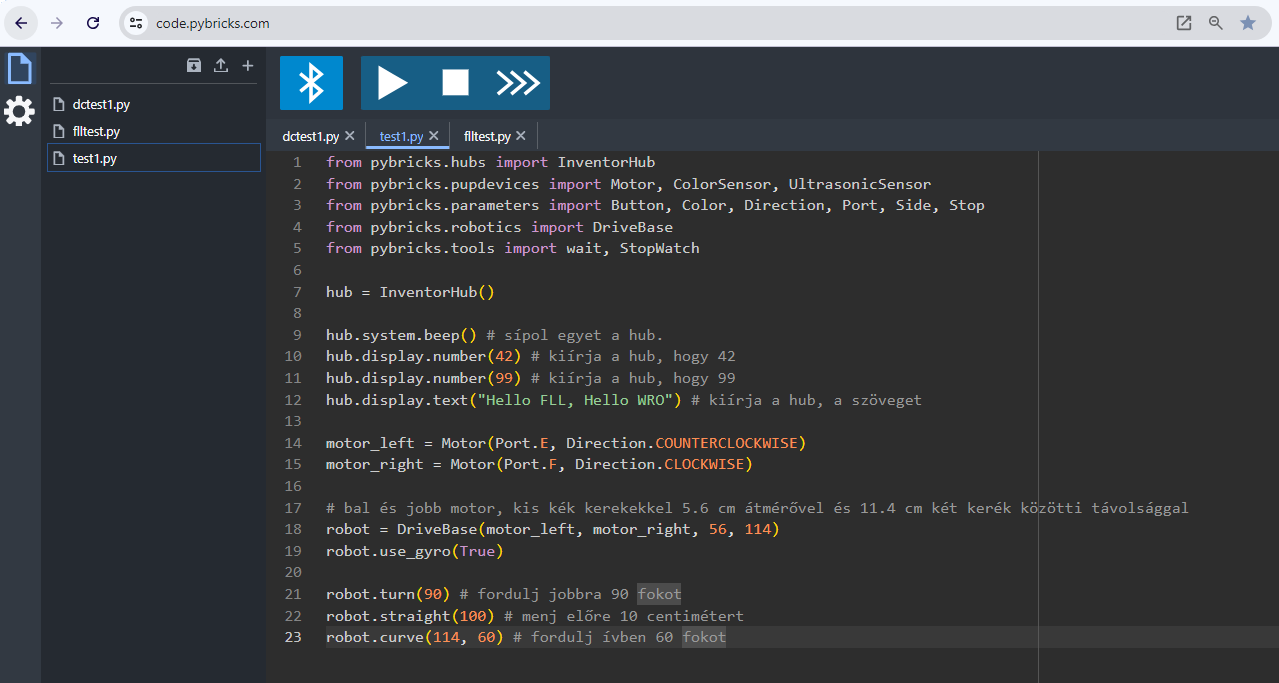
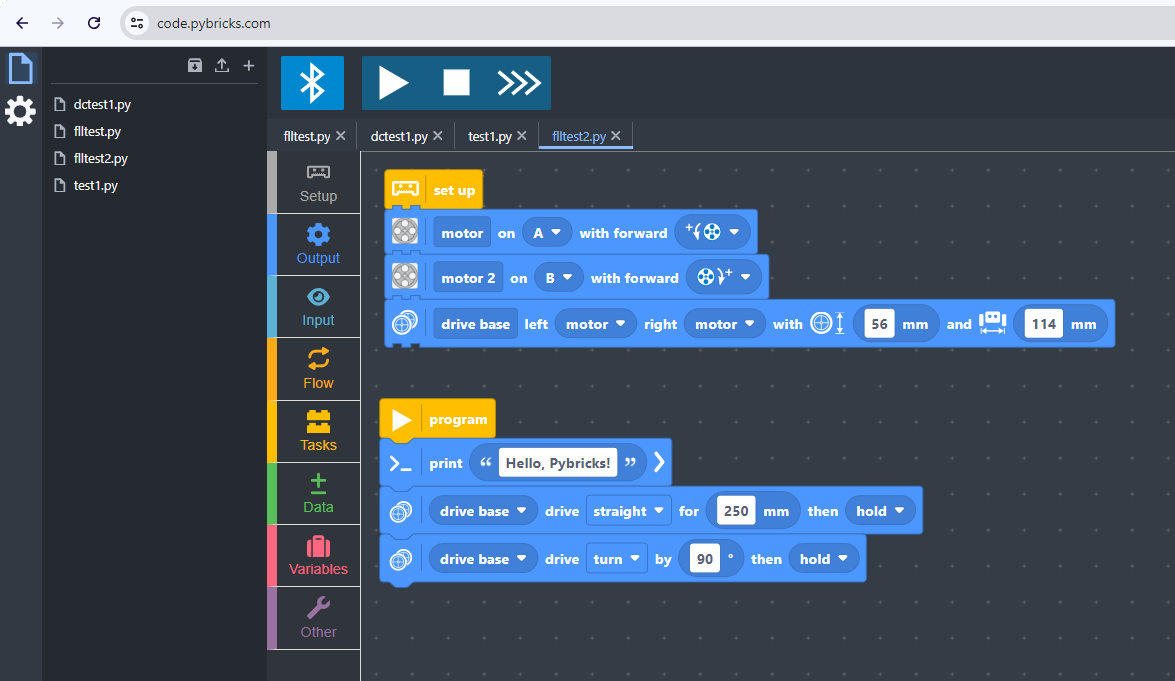
Pybricks has made these capabilities also available in a block-based environment that is not completely free but requires a recurring or one-time payment. I have purchased the license because we have gained so much from this framework and simply wanted to experiment and pay back.
I recommend that if you can, you also support the further development of Pybricks.
References
- Pál Bodnár
- Some of the tutorial tasks were inspired by the Python tutorial of Pál Bodnár, programming teacher and robotics enthusiast.
Check out his tutorials on his youtube channel.
END OF THIS TUTORIAL.